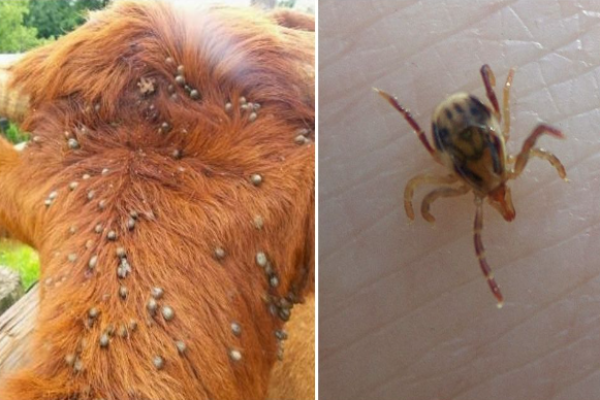
Lice In Cattle
Lice irritate cattle, causing the cattle to bite, scratch and rub. This constant irritation can become a welfare issue. ...

Ketosis
A disease of ruminants which is the result of a failure to metabolise carbohydrate and volatile fatty acids, and characterised by high blood ketone and low blood glucose levels, mainly in high producing dairy cattle in the first two months of lactation....

Foot Rot
Foot rot; the earliest sign is a swelling and moistening of the skin of the interdigital cleft particularly in the region of the heel. This is soon followed by a break in the skin-horn junction and then a separation of the adjacent soft horn....

Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is a severe, highly contagious viral disease of cattle and swine. It also affects sheep, goats, deer, and other cloven-hooved ruminants. The virus can persist in contaminated fodder and the environment for up to one month...

Foot Abscess
Foot abscesses often develop when the soil and pastures are wet or frozen. The disease causes an acute lameness that is usually restricted to one foot, which the sheep will not place on the ground....

Fog Fever
Fog Fever is one of the most common respiratory diseases of grazing adult beef cows. This is a sudden onset, respiratory distress syndrome with minimal coughing which occurs typically in hungry fat, beef-type cows, in the autumn, within two weeks of their...

Enterotoxaemia (Pulpy Kidney)
Enterotoxaemia is a severe disease affecting sheep, it less frequently affects goats and is rarely seen in cattle. ...

Cobalt Deficiency
Cobalt deficiency in sheep, disease of young stock occurring mostly in spring and early summer....

Botulism
Botulism; Occurs when potent toxins are produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Early signs are uncoordination, loss of appetite, excessive salivation, mild excitability and nervous twitching and jaw champing....

Blackleg Disease
Blackleg is an acute fatal disease of young cattle characterised by the development of swelling in the upper muscle masses of one or more limbs. The animals affected are frequently those in good condition and on a high plane of nutrition....

Written by
H Cetin KATIRCI
Ask for Help From Our Community
IllnessesMore
Forage cropsMore
![]() Патологическая физиология голодания Arina TARAN
Патологическая физиология голодания Arina TARAN![]() Дефицит фосфора (гипофосфатемия) Hipofosfatemi Arina TARAN
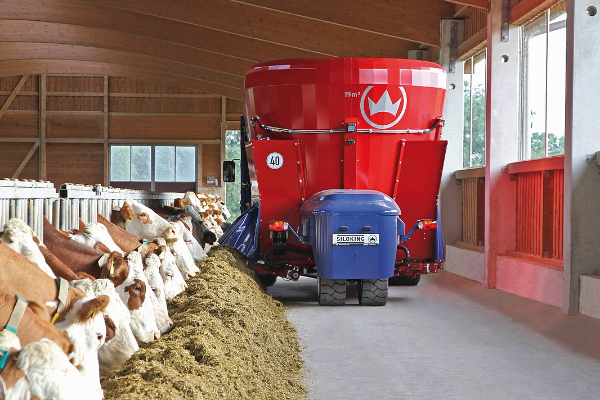
Дефицит фосфора (гипофосфатемия) Hipofosfatemi Arina TARAN![]() Какие бывают кормораздатчики для ферм КРС? Irina Makarova
Какие бывают кормораздатчики для ферм КРС? Irina Makarova![]() Кормушки для овец Diana Myakisheva
Кормушки для овец Diana Myakisheva![]() Питание домашних коз: что едят, виды корма и правила кормления Alina Arslantürk
Питание домашних коз: что едят, виды корма и правила кормления Alina Arslantürk![]() Важность минералов питании сельскохозяйственных животных Irina Makarova
Важность минералов питании сельскохозяйственных животных Irina Makarova












